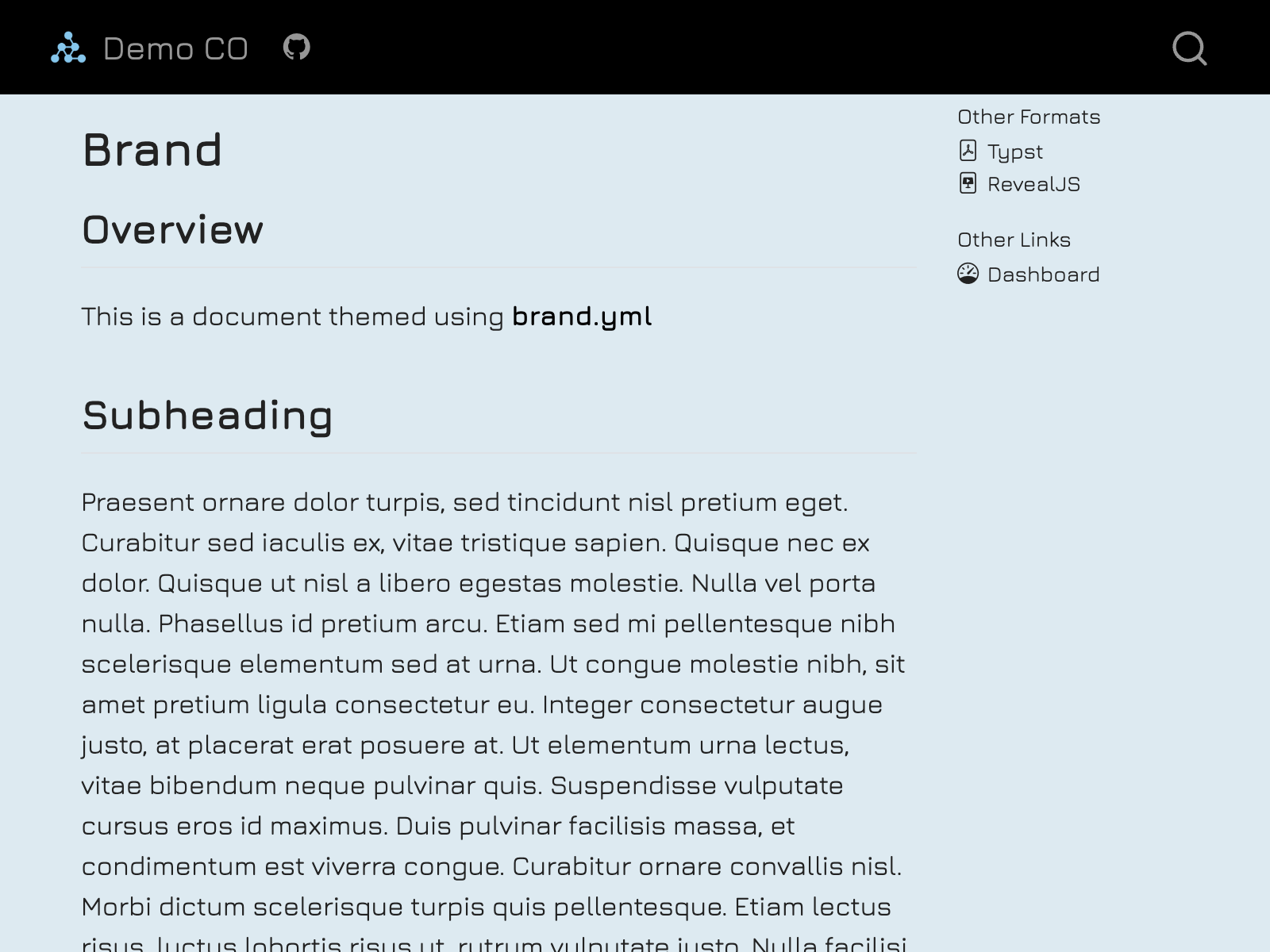
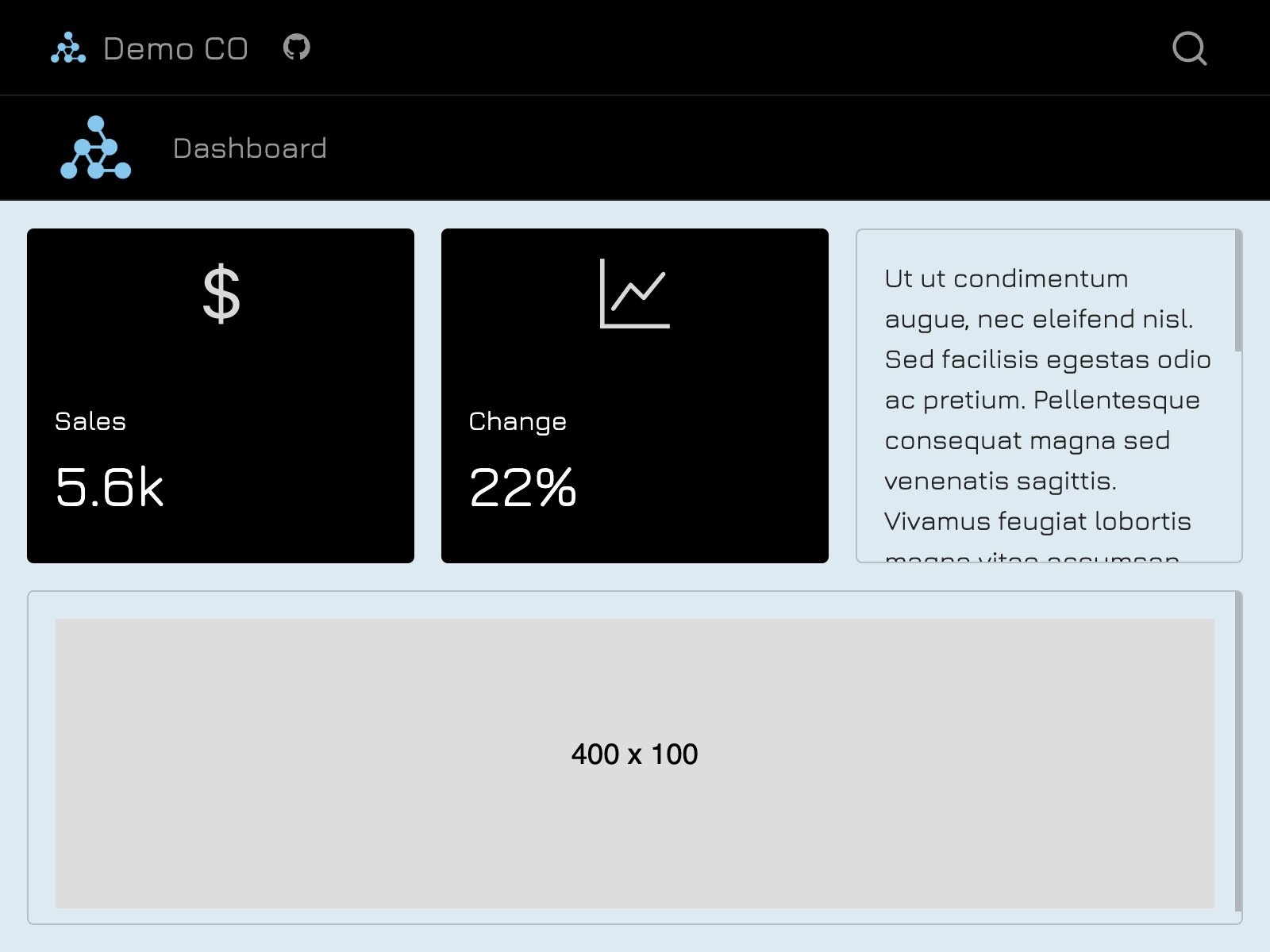
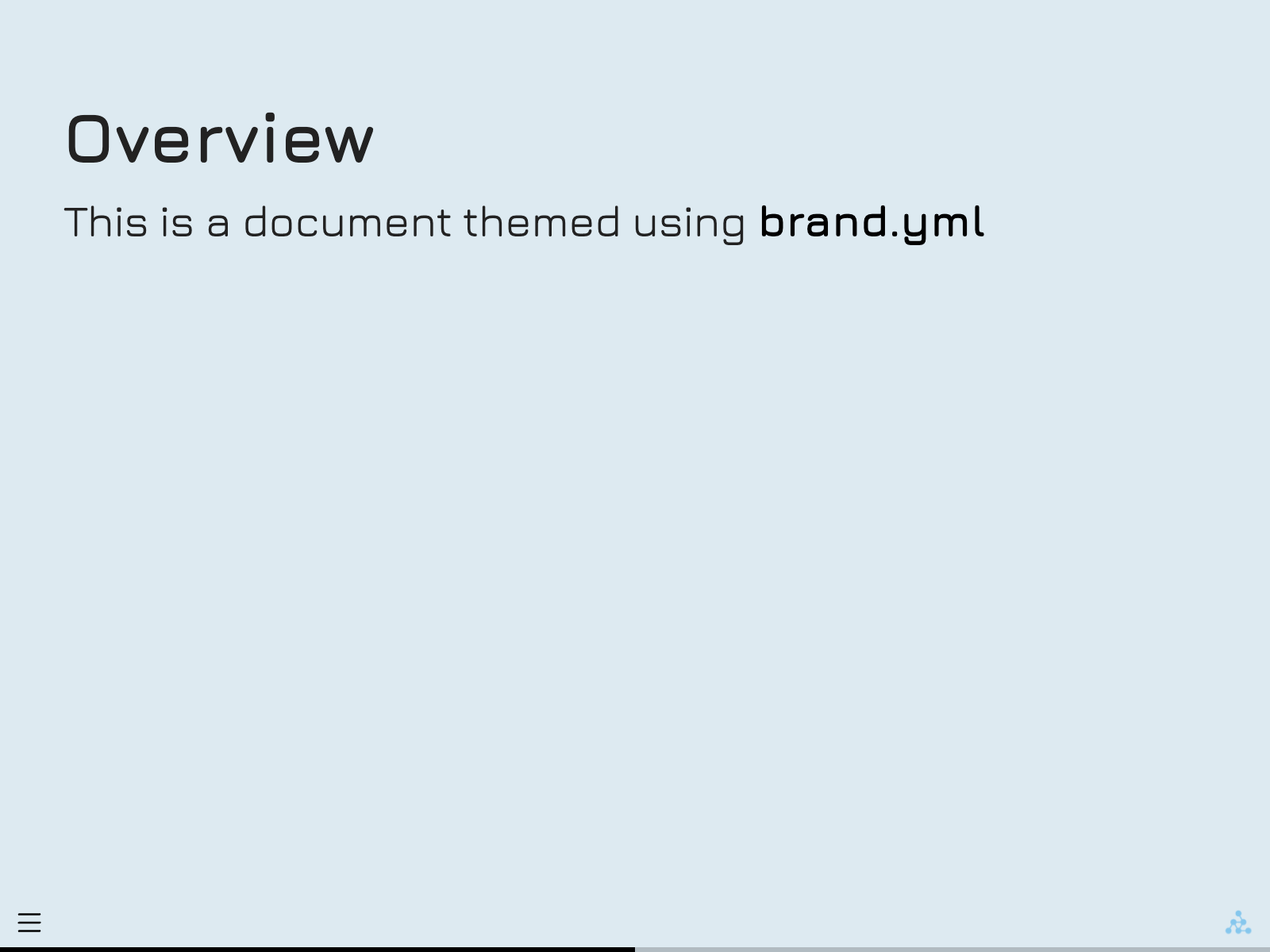
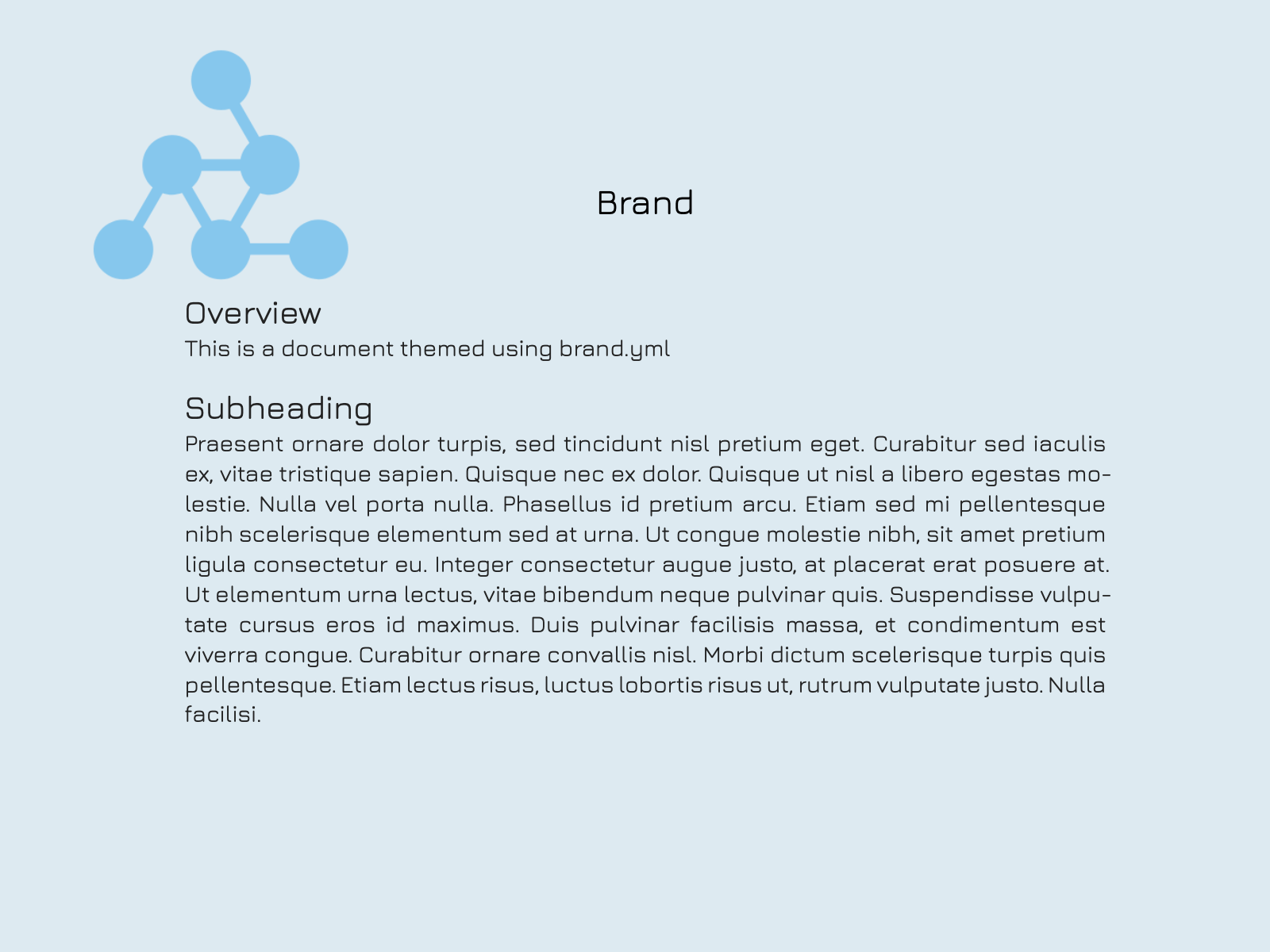
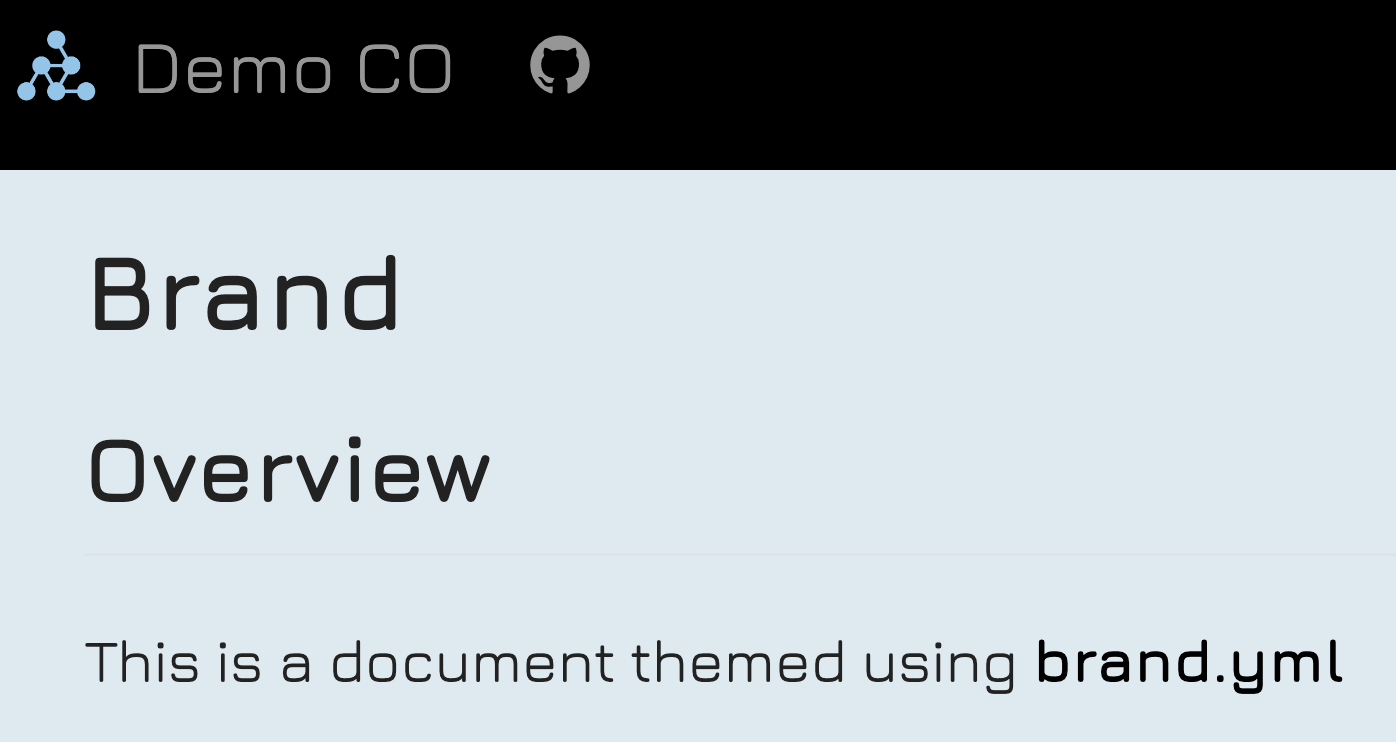
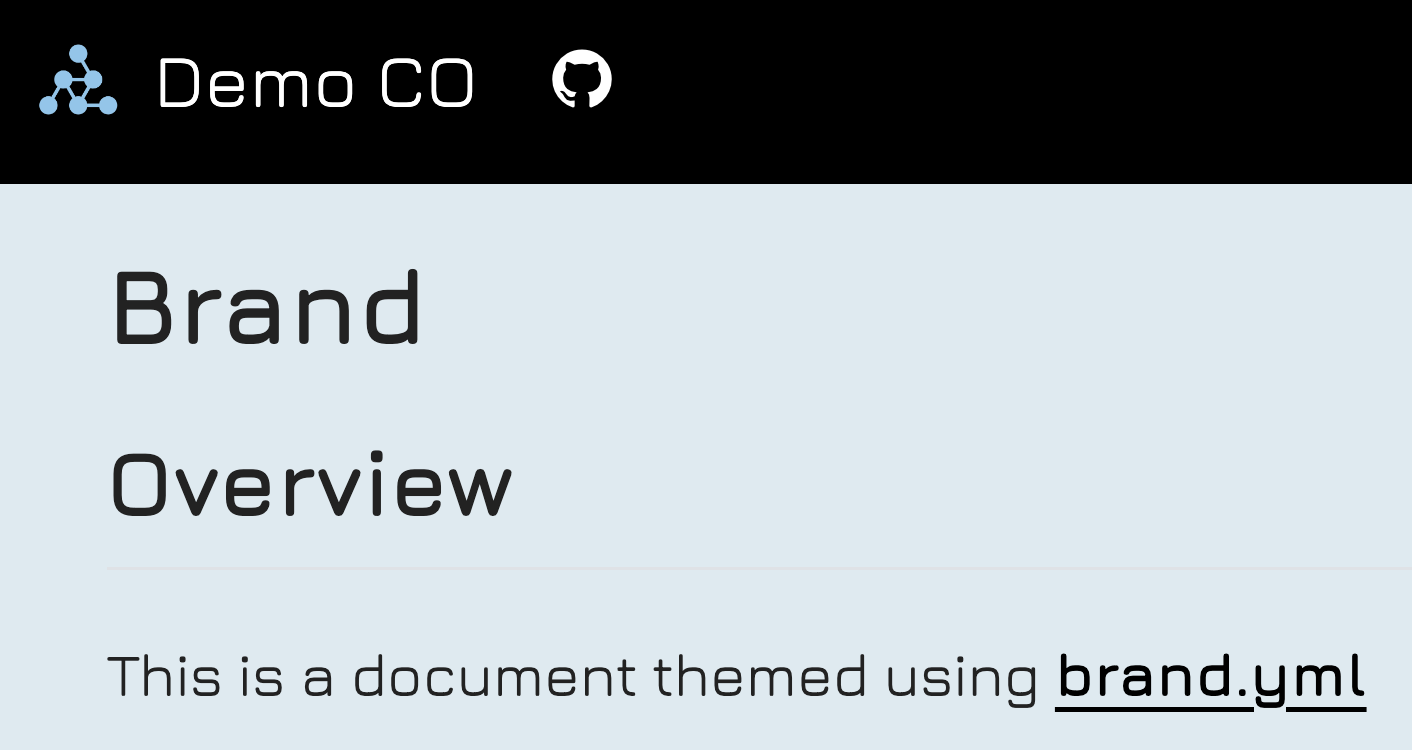
Multiformat branding with _brand.yml
Overview
Quarto supports brand.yml—a single YAML file that can be used to customize the appearance of your documents across multiple formats. This is particularly useful for organizations that need a unified look across various formats.
As an example, consider the following _brand.yml file:
_brand.yml
color:
palette:
dark-grey: "#222222"
blue: "#ddeaf1"
background: blue
foreground: dark-grey
primary: black
logo:
medium: logo.png
typography:
fonts:
- family: Jura
source: google
base: Jura
headings: JuraWhen this _brand.yml is placed in a project, webpages, presentations, PDF reports, and dashboards will share a common appearance:
View the example: Source | Live website
On this page:
Learn how to add a brand file.
Learn about the elements of brand.yml and how they are used in Quarto.
Learn how to access brand values outside of the brand file.
See a more comprehensive example.
Learn how to migrate projects created without
_brand.ymlto easily support_brand.ymlfeatures.
The brand.yml specification is an active area of work at Posit. Quarto’s support for brand.yml is not yet complete. For now, we’ve highlighted places where Quarto doesn’t yet support the full spec with special Limitation callouts, like this one.
Currently, the formats that support brand.yml are: html, dashboard, revealjs and typst.
Applying Brand
To specify a brand, create a _brand.yml file in the root directory of your project (i.e. alongside _quarto.yml). Quarto will detect the presence of _brand.yml and automatically apply the brand to all documents of the supported formats in the project.
You can create a _brand.yml file outside of a Quarto project (e.g. without a _quarto.yml). In this case, _brand.yml will automatically apply to documents in the same directory.
_brand.yml
color:
background: "#eeeeee"You can also set brand options in a document by specifying brand elements under the brand option:
document.qmd
---
brand:
color:
background: "#eeeeee"
---If you set brand in a document header, it will replace the entire brand from _brand.yml.
You can disable brand for a document by setting brand to false:
document.qmd
---
brand: false
---You can put _brand.yml in a subdirectory of your project, and then use the brand key to specify the path to the brand file. For example, to use the brand file at brand/_brand.yml for a single document, add brand to the header:
document.qmd
---
brand: brand/_brand.yml
---To use the brand file at brand/_brand.yml for all documents in the project add brand to _quarto.yml:
_quarto.yml
brand: brand/_brand.ymlPaths specified in _brand.yml are relative to the location of the brand file.
Light and Dark Colors
To specify colors for both light and dark modes using a single brand.yml file, specify any color in color or typography with an object containing the light and dark colors:
_brand.yml
color:
background:
light: "#ffffff"
dark: "#333333"
foreground:
light: "#333333"
dark: "#ffffff"
typography:
headings:
color:
light: "#111144"
dark: "#d0d0ff"This also works with the brand specified directly in the document metadata:
document.qmd
---
brand:
color:
background:
light: "#ffffff"
dark: "#333333"
foreground:
light: "#333333"
dark: "#ffffff"
typography:
headings:
color:
light: "#111144"
dark: "#d0d0ff"
---Colors in the palette cannot currently be specified with light and dark variants.
Light and Dark Brands
If you prefer to author separate light and dark brands for light and dark mode, or you need to customize non-color properties, you can separate the brands into their own files, and specify light and dark brand files:
document.qmd
---
brand:
light: light-brand.yml
dark: dark-brand.yml
---This is similar to how Themes work.
This also works with brands specified directly in the document:
document.qmd
---
brand:
light:
color:
background: "#ffffff"
foreground: "#333333"
dark:
color:
background: "#333333"
foreground: "#ffffff"
---Light and dark brands can also be specified at the project-level:
_quarto.yml
brand:
light: light-brand.yml
dark: dark-brand.ymlBrand metadata cannot currently be specified directly in _quarto.yml, only via the file syntax.
Brand Mode
The Typst and revealjs formats do not produce outputs which can toggle between light and dark mode dynamically.
By default, Typst and revealjs formats will render using the light brand. Set brand-mode: dark to render using the dark brand.
Typst:
document.qmd
---
format:
typst:
brand-mode: dark
---Revealjs:
document.qmd
---
format:
revealjs:
brand-mode: dark
---Brand Elements
The elements of brand.yml are specified in the documentation for the brand.yml project. In this section, learn how these elements are used in Quarto.
Color
Use color to define your brand’s color palette and map your palette to the roles colors play, a.k.a semantic colors. A simple example might define the value background to a light blue:
_brand.yml
color:
background: "#ddeaf1"Use the palette key to define a set of named colors that can be referenced elsewhere in the _brand.yml. For example, you might define blue and set it as the background:
_brand.yml
color:
palette:
blue: "#ddeaf1"
background: blueThe most commonly used semantic colors include foreground, background and primary:
_brand.yml
color:
palette:
dark-grey: "#222222"
blue: "#ddeaf1"
background: blue
foreground: dark-grey
primary: blackThe colors foreground and background are used consistently across formats to set the color of the main text and color of the page it appears on. The color primary sets the link color, navbar color (html and dashboard), and progress bar color (revealjs).
For HTML formats that use Bootstrap (html, dashboard) the remaining semantic colors are mapped directly to their Bootstrap counterparts with the same name.
The full list of semantic colors you can set in color is:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
foreground |
The main text color. Typically will be close to black and must have high contrast with the background color. |
background |
The main background color. Tyically will be close to white and must have high contrast with the foreground color. |
primary |
The primary accent color, used for hyperlinks, active states, and primary action buttons. |
secondary |
The secondary accent color, often used for lighter text or disabled states. |
tertiary |
The tertiary accent color, used for hover states, accents, and wells. |
success |
The color used for positive or successful actions and information. |
info |
The color used for neutral or informational actions and information. |
warning |
The color used for warning or cautionary actions and information. |
danger |
The color used for errors, dangerous actions, or negative information. |
light |
A bright color, used as a high-contrast foreground color on dark elements or low-contrast background color on light elements. |
dark |
A dark color, used as a high-contrast foreground color on light elements or high-contrast background color on light elements. |
You can access both named and semantic colors from your brand in SCSS and using the brand shortcode. See Using _brand.yml values for more details.
Logo
Use logo to specify the logo for your brand:
_brand.yml
logo:
medium: logo.pngYou can specify a local file path, relative to the location of _brand.yml, or a URL.
A single logo may not work well in all locations so brand.yml allows you to set three different logos: small, medium and large. For example:
_brand.yml
logo:
small: logo-small.png
medium: logo.png
large: logo-large.pngYou don’t need to specify all three—Quarto will use what you provide based on the following preferences:
| Format | Location | Logo Preference (high to low) |
|---|---|---|
html/dashboard |
Top navigation bar | small> medium>large |
html |
Side navigation | medium>small>large |
typst |
Top left, control with format: typst: logo |
medium>small>large |
revealjs |
Bottom right corner of slides | medium>small>large |
website/book project |
favicon shown in browser tab |
small |
You can also specify named logos under images which you can reference in small, medium and large. In particular, this allows you to set alternative text for your logos using alt:
_brand.yml
logo:
images:
quarto-logo:
path: https://quarto.org/quarto.png
alt: "Quarto icon"
small: quarto-logoLight and Dark Logos
Specify different logos for light and dark mode with light and dark options under small, medium, or large:
_brand.yml
logo:
medium:
light: logo.png
dark: logo-white.pngDocument logo customization
You can further customize the logo at the document level with the logo option.
For example, you can specify a particular brand logo resource:
document.qmd
---
logo: large
---Or override the brand logo for this document with a logo from a file:
document.qmd
---
logo: logo.png
---Or specify a brand logo resource and change the alt text:
document.qmd
---
logo:
path: large
alt: Alternate alternate text
---You can also individually customize light and dark logos, with any of the variations shown above:
document.qmd
---
logo:
light:
path: large
alt: Alternate alternate text
dark:
path: dark-logo.png
alt: Alternate text for dark logo
---It is not currently possible to customize the logo for a specific page within a website. Only the project’s _brand.yml is applied.
When using format: typst you can additionally customize the logo position.
Typography
Typography in the brand.yml docs
The typography element allows you to specify fonts and their style. Use fonts to specify a list of fonts to use for your brand:
_brand.yml
typography:
fonts:
- family: Jura
source: googleThe properties you can set for a font under fonts depends on the source. You can see the other properties available in our Reference for Brand.
You can then refer to fonts by family in the remaining typography options:
_brand.yml
typography:
fonts:
- family: Jura
source: google
base: Jura
headings: JuraThe options base and headings set the typographic style of the main text and headings respectively. Use links to apply specific styles to links. The option monospace sets the typographic style of code in general, and monospace-inline and monospace-block can be further used to style code that appears inline and in blocks respectively:
_brand.yml
typography:
fonts:
- family: Jura
source: google
- family: Space Mono
source: google
base: Jura
headings: Jura
link:
decoration: underline
monospace: Space Mono
monospace-inline:
color: "#222222"
background-color: "#ddeaf1" # or use a named color from `color`
monospace-block:
background-color: "#eef4f8"The fields allowed for each element differ, expand the callout below to see what is supported in each field.
The full set of text elements that you can style with typography is:
| Attribute | Description | Supported Fields |
|---|---|---|
base |
Default text, primarily used in the document body. |
|
headings |
All heading levels (h1, h2, etc.). |
|
monospace |
General monospaced text, typically used in code blocks and other programming-related content. |
|
monospace-inline |
Inline monospaced text, usually used for code snippets within regular text. Inherits from monospace. |
|
monospace-block |
Block (multi-line) monospaced text, typically used for code blocks. Inherits from monospace. |
|
link |
Hyperlinks. |
|
The supported fields are generally described as follows:
family: The font family to be used for a typographic element. This should match a font resource declared intypography.fonts.size: The font size for a typographic element. Should be specified using a CSS length unit (e.g., “14px”, “1em”, “0.9rem”).weight: The font weight (or boldness) of the text. Can be a numeric value between 100 and 900, or a string like “normal” or “bold”.style: The font style for the text, typically either “normal” or “italic”.line-height: The line height of the text, which refers to the vertical space between lines. Often expressed as a multiple of the font size or in fixed units.color: The color of the text. Can be any CSS-compatible color definition or a reference to a color defined in the brand’s color palette.background-color: The background color for the text element. Can be any CSS-compatible color definition or a reference to a color defined in the brand’s color palette.decoration: The text decoration, typically used for links. Common values include “underline”, “none”, or “overline”.
Typst
See the Advanced documentation for more details on the Typst implementation, and troubleshooting tips for fonts.
Defaults
Defaults in the brand.yml docs
The defaults section of brand.yml allows users to set options for specific tools that don’t otherwise fit into the brand.yml schema. Quarto’s implementation currently supports defaults: bootstrap.
Bootstrap
The bootstrap section of defaults follows brand.yml and applies to the html and dashboard formats. Quarto merges the options set under defaults: bootstrap in the appropriate layer of Quarto’s SCSS layering system.
The defaults option inside bootstrap, can take a string, or key-value pairs corresponding to SCSS variable name-value pairs. Building on our initial example, you could use bootstrap: defaults to set the SCSS variables link-decoration and navbar-fg:
_brand.yml
defaults:
bootstrap:
defaults: # defaults also supports a string as its value
link-decoration: underline
navbar-fg: "#fff"The resulting HTML pages will have links that are underlined and use white for text in the navigation bar.
In addition to the defaults option, Quarto supports uses, functions, mixins and rules, which all take a string value. For example, you could use rules to provide a CSS rule to remove the border below second-level headings:
_brand.yml
defaults:
bootstrap:
# uses: <string>
# functions: <string>
# mixins: <string>
rules: |
h2 {
border: none;
}Meta
You can set brand metadata using the meta key:
_brand.yml
meta:
name: Acme Corporation
link: https://www.acmecorp.comQuarto does nothing with meta values.
Using _brand.yml values
Beyond the automatic application of your brand file, you can also directly access _brand.yml values in Quarto documents. In this section, you’ll learn how to use the brand shortcode, use brand variables in SCSS files, and some format-specific ways to use access brand values.
Shortcode - {{< brand >}}
Some values from the _brand.yml configuration file can be accessed via the brand shortcode. In particular, you can access colors and logos by name:
- Use
{{< brand color COLOR_NAME VARIANT >}}to return the brand color namedCOLOR_NAMEas a string. - Use
{{< brand logo LOGO_NAME VARIANT >}}to return the brand logo namedLOGO_NAMEas an image.
VARIANT is optional:
- For the
brand colorshortcode, the default islight. To return the color from the dark brand usedark. - For the
brand logoshortcode, the default isboth, which will expand to both light and dark logos with the appropriate classes for mode-specific content so that the light logo shows in light mode and the dark logo shows in dark mode.
If the VARIANT is light or dark, the brand logo shortcode will not add a mode-specific class.
For example, you could use the shortcode to place a brand image you’ve named icon in a dashboard sidebar:
dashboard.qmd
---
format: dashboard
---
## Inputs {.sidebar}
{{< brand logo icon >}}Or, you could use the shortcode to set the background of a revealjs slide to your primary brand color:
slides.qmd
---
format: revealjs
---
## Slide Title {background-color='{{< brand color primary >}}'}You can’t currently access typography, meta, or defaults values using the brand shortcode.
In SCSS
The colors defined in palette are set as SCSS variables of the form brand-COLOR_NAME. For example, if _brand.yml defines blue:
_brand.yml
color:
palette:
blue: "#ddeaf1"Then the variable $brand-blue is will be set to #ddeaf1 in the defaults layer of Quarto’s SCSS layering system. You can add a custom SCSS file, styles.scss, in the usual way:
_quarto.yml
format:
html:
theme: [styles.scss]Then styles.scss can use these brand variables to make style tweaks. For example, you might want all h1 elements to be blue:
styles.scss
/*-- scss:rules --*/
h1 {
color: $brand-blue;
}When you specify SCSS files without an explicit brand element, it is equivalent to listing them after brand. For instance, the above theme is equivalent to:
_quarto.yml
format:
html:
theme: [brand, styles.scss]The order of elements in theme controls their priority. For example, you could layer brand and your custom SCSS on top of a built-in theme:
_quarto.yml
format:
html:
theme: [cosmo, brand, styles.scss]You can learn more about layering themes in More About Quarto Themes.
Typst
In Typst documents, brand colors are set in a dictionary called brand-color. You can access them directory in raw Typst blocks using the syntax brand-color.COLOR_NAME. For example, you could make a rectangle filled with your primary brand color:
document.qmd
```{=typst}
#rect(fill: brand-color.primary)
```Brand logos are set in dictionaries called brand-logo and brand-logo-images.
For example, you can write Typst code to insert an image using its resolved path and alt text from brand.logo.images:
document.qmd
---
format: typst
brand:
logo:
images:
custom:
path: custom.png
alt: custom logo
---
```{=typst}
#image(brand-logo-images.custom.path, alt=brand-logo-images.custom.alt)
```Lua API
Filters and shortcodes can access brand values using the brand Lua module.
local brand = require('modules/brand/brand')
local primary = brand.get_color('primary')Combining brands and themes
The following information is only necessary if you want to combine bootswatch themes with _brand.yml.
Migrating existing projects to Quarto 1.6’s _brand.yml support is a straightforward process. The usual way to create themes in Quarto 1.5 and earlier is to use one of the predefined bootswatch themes. This is often combined with an additional user-defined .scss file. In Quarto 1.5, a _quarto.yml file usually has an entry like the following:
# Quarto 1.5 syntax
theme:
- cosmo # a predefined bootswatch theme
- tweaks.scss # a user-defined customizationWhen using this syntax with Quarto 1.6’s _brand.yml support, keep in mind that _brand.yml always takes lowest priority in styles. In other words, the configuration above is equivalent to the following:
# Quarto 1.6 syntax
theme:
- brand # theming derived from `_brand.yml`
- cosmo # a predefined bootswatch theme
- tweaks.scss # a user-defined customizationAs a result, values set by brand here are potentially overriden by the cosmo theme or by tweaks.scss. This is sometimes useful, but often you will want to make brand more important than the theme. For these situations, use the following:
# Quarto 1.6 syntax
theme:
- cosmo # a predefined bootswatch theme
- brand # theming derived from `_brand.yml`
- tweaks.scss # a user-defined customizationThe analogous syntax also works for combining light and dark brands with light and dark themes:
# Quarto 1.7 syntax
theme:
light:
- cosmo
- brand
dark:
- slate
- brandLearn more about how Quarto generates styles in More About Quarto Themes.